Types of Computer Network Topologies: Bus, Star, and Ring
What is a Network Topology?
Topology is a characteristic of a Local Area Network. It is both the physical configuration of the cabling used to connect computers in the network, and the logical way in which the system views the structure of the network. Topology is therefore the physical or logical arrangement of computers.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Topology
- Cost. The transmission medium chosen for a Local Area Network has to be physically installed in the building, using cables and raceways. To make the network cost effective, it's desirable to minimize installation cost. This may be done by using the correct hardware to link the cables, good modems, and cost-effective computers.
- Flexibility. One of the main benefits of a Local Area Network is the ability to distribute the data processing and peripheral nodes around a given area. It can locate the computing power and equipment close to the ultimate users. Because in an office, the arrangement of furniture and internal walls is often subject to change, the topology should allow for easy reconstruction of the network when nodes are moved or added.
- Reliability – The topology chosen for the network can help locate faults by allowing the fault to be detected and isolated.
Types of Network Topology
Below we discuss the three main types of network topology.
Star Topology (Also Called Radial Topology)
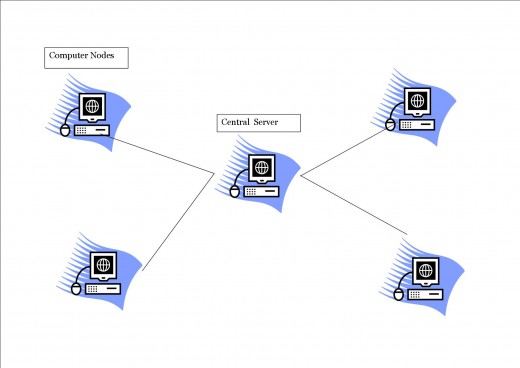
This topology includes a central node to which all other nodes are connected. Star topology is used in most existing information networks that involve data processing and voice communication. In many cases when a building is wired with a star topology, faced cables radiate out from the center to intermediate connection points to wiring cables. This allows sufficient connection points to be provided for one subarea, while providing flexibility in the allocation of the connection points within that area.
Advantages of Star Topology
- Easy diagnosis and isolation of problems
- Easy to add a new computer system to the network
- Failure of one workstation does not affect the entire network
- Uses a single access protocol
- Ease of service
- Speed
Disadvantages of Star Topology
- Depends on a central node
- Adding nodes can be costly
- Requires long cables to connect many nodes
Bus Topology (Also Called "Linear Topology")
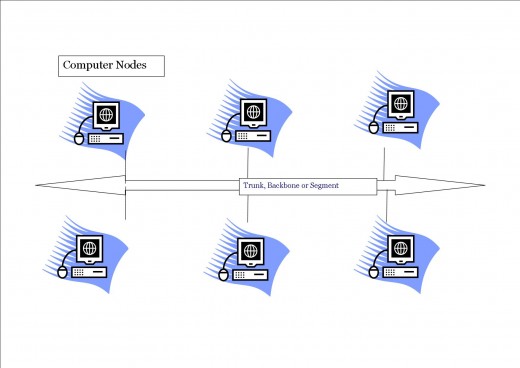
Bus topology is the simplest method of networking computers. It consists of a single cable, known as a trunk, backbone, or segment, that connects all the computers in the network. Each system is directly attached to a common communication channel. Messages consist of a signal transmitted over the channel. As the message passes along the channel each system receives it and then examines the destination address contained in the message. If the destination address tells a particular system that the message is addressed to it, that system accepts and processes the message; if the message address tells the computer that the message is intended for another system, the computer will ignore the message.
On a bus topology, signals are sent to all the computers in the network. To keep the signal from bouncing back and forth along the cable a terminator (a British Naval Connector) is placed at the end of the cable. In a bus topology only one computer can send data at a time; therefore, the more computers in a bus, the slower data is transmitted in the network.
Advantages of Bus Topology
- Cheap because of its simplicity
- Requires a short cable length
- Easy to expand the network
- Simple to set up compared to Star and Ring topology
- No chance of data collision, since one computer transmits at a time
- Locating a cable fault is relatively easy
- Ideal for one-to-many data transmission
- Signals on the cable are bidirectional, so they reach all the nodes
Disadvantages of Bus Topology
- Fault diagnosis is difficult, because fault detection may have to be performed from any point in the network.
- Fault isolation is difficult, because if the fault is detected in a node the node can simply be removed, but if the fault is in the network medium itself, an entire segment of the bus must be disconnected to isolate the fault
- Repeater configuration may be necessary. When the backbone of a bus type network uses a repeater, it may be necessary to tailor the cable length and adjust the terminator.
- Computer nodes must be intelligent. Because each node on the network is directly connected to the central bus, each node must have a method of identifying its own data.
Ring Topology
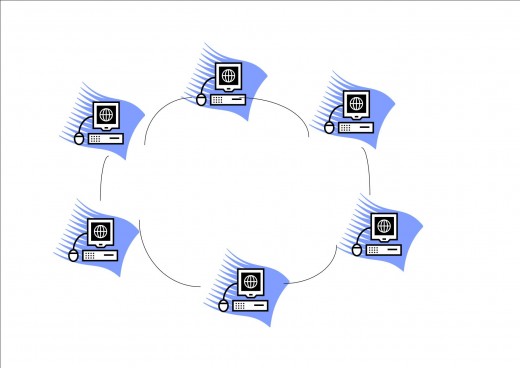
In ring topology, each node is connected to form a single closed data path. Data from one node is passed along to the next node, which examines it. If that node is not the intended destination, then the data is transmitted to the next node until the destination is reached. A token (a special bit pattern) is circulated in the network to enable a node to capture the data. Ring topology might be structured so that there are a number of information frames or slots in constant circulation. A node wishing to transmit first detects the arrival of an empty slot, then inserts the data it wishes to send, and marks the frame as full. The receiving node takes the data and then marks the frame as empty. In implementation, when the network is first constituted, one particular node is given the responsibility for generating the token or slot.
Advantages of Ring Topology
- The ability to achieve transmission rates on the order of 10 million bits per second
- Provision of local communication via a single channel
- No central server (which reduces the cost)
Disadvantages of Ring Topology
- Failure of one node results in failure of the entire network
- Detection of a fault is very difficult
- Isolation of a fault is not easy